“When Cold Chain Becomes Indispensable for a Retail Pharmacist”
In India, at least 25 per cent of the vaccines go waste even before reaching the doctor or the patient while many lose their efficacy by the time they are administered due to lack of quality supply chain and logistics management system.
Thermolabile biologics demand absolute precision, yet they remain highly susceptible to unhindered disruptions—sudden power failures, equipment malfunctions, voltage fluctuations, and unnoticed temperature excursions—which strike without warning.
These failures often go undetected until it’s too late, delaying corrective action and leading to irreversible potency loss and financial setbacks.
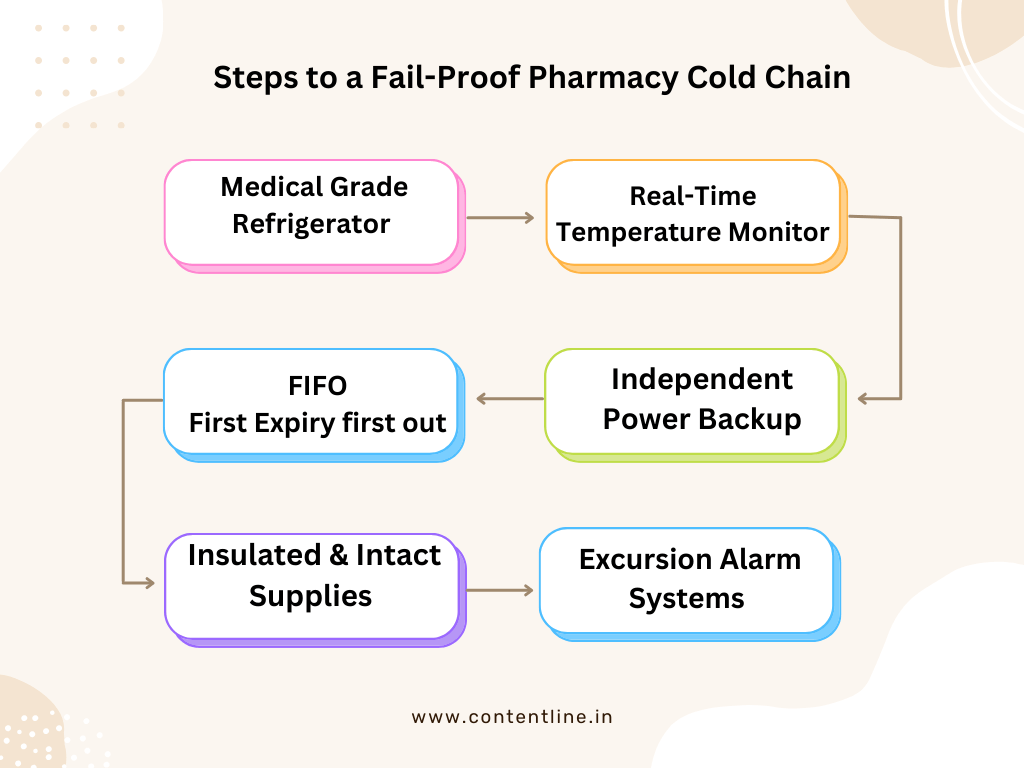
Preserve with Precision: Install a Medical-Grade Refrigerator
- Select a validated medical-grade refrigeration unit designed for precise temperature control.
- Ensure it meets regulatory standards for pharmaceutical and biological storage.
Proactive Temperature Management
- Equip the refrigerator with a calibrated digital thermometer.
- Implement a real-time temperature monitoring system with data logging capabilities.
Powering Refrigeration Beyond Outages
- Avoid connecting refrigerators to the main server to prevent accidental shutdowns.
- Ensure that refrigeration units have an independent power backup.
Proper Vaccine Storage and Handling
- Organize stock based on expiry dates to follow the First Expiry First Out (FEFO) principle.
- Avoid overloading and frequent door openings.
Insulated Supply Packaging
- Receive Supplies in Insulated Packaging.
- Use insulated or thermocol boxes to maintain required temperatures during transportation.
- Verify temperature compliance upon receipt with data loggers or temperature indicators.
- Check that the temperatures in the insulated boxes remain consistent to avoid thermal shock or cryogenic stress.
Implement Excursion Alarm Systems
- Set up alarms to detect and notify personnel of any temperature deviations.
- Integrate voltage fluctuation alerts to prevent potential refrigeration failures.
Regular Maintenance and Calibration
- Perform periodic calibration of temperature monitoring devices.
- Conduct routine maintenance checks on refrigeration and power backup systems